Rosacea is a long-term inflammatory skin condition that mainly affects the face and can significantly impact a person’s confidence and quality of life. It often appears as persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and acne-like bumps, especially on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. Although rosacea is not contagious, it tends to worsen over time if left untreated. Early recognition and proper management play a crucial role in controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Understanding rosacea, its triggers, and treatment options can help patients maintain healthier, calmer skin.
What Is Rosacea?
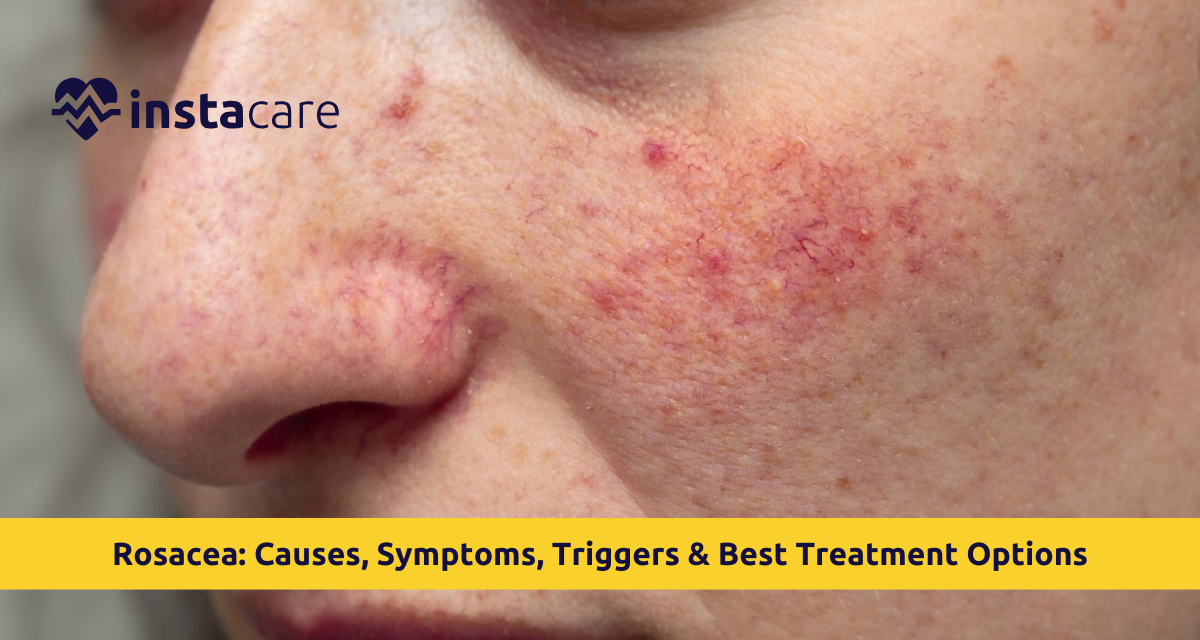
Rosacea is a chronic skin disorder characterized by facial redness, flushing, and inflammation. It commonly affects adults between the ages of 30 and 50 and is more noticeable in people with fair skin, though it can occur in all skin types. Unlike temporary redness caused by heat or embarrassment, rosacea redness tends to persist and may gradually become permanent. Over time, untreated rosacea can lead to thickened skin, eye irritation, and visible blood vessels. Because symptoms can resemble acne or allergic reactions, rosacea is often misdiagnosed, delaying effective treatment.
Common Symptoms of Rosacea
The symptoms of rosacea vary from person to person and may change over time. The most common sign is persistent facial redness, particularly across the cheeks and nose. Many patients also experience frequent flushing, burning, or stinging sensations. Small red bumps and pus-filled pimples may appear, often mistaken for acne, but without blackheads. In some cases, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia) develop on the skin surface. Advanced rosacea can cause thickened skin, especially on the nose, and may also lead to eye problems such as dryness, irritation, and redness.
Causes and Risk Factors of Rosacea
The exact cause of rosacea is still not fully understood, but experts believe it results from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Abnormal blood vessel function, inflammation, and an overactive immune response are thought to play a role. Certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing rosacea, including a family history of the condition, fair skin, and age. External triggers such as sun exposure, hot weather, spicy foods, alcohol, stress, and harsh skincare products can worsen symptoms and cause flare-ups.
Different Types of Rosacea
Rosacea is not a single condition but includes several subtypes, each with distinct features. Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea mainly causes redness and visible blood vessels. Papulopustular rosacea presents with acne-like breakouts along with redness. Phymatous rosacea leads to thickened, bumpy skin, most commonly affecting the nose. Ocular rosacea affects the eyes, causing dryness, irritation, and sensitivity to light. Identifying the specific type of rosacea is important because treatment approaches may differ depending on the symptoms and severity.
How Rosacea Is Diagnosed
Rosacea is usually diagnosed through a clinical examination by a dermatologist. There is no specific laboratory test for rosacea, so diagnosis is based on visible symptoms, medical history, and trigger patterns. A dermatologist will carefully examine the skin and may ask about flushing episodes, skincare habits, and lifestyle factors. In some cases, additional tests may be done to rule out conditions like lupus or acne. Early and accurate diagnosis helps prevent progression and allows for a more targeted and effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Rosacea
While rosacea has no permanent cure, many effective treatments can control symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Topical medications such as metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin are commonly prescribed to reduce redness and inflammation. Oral antibiotics may be used for moderate to severe cases. Laser and light-based therapies can help reduce visible blood vessels and persistent redness. Treatment plans are usually customized based on the type and severity of rosacea, making professional dermatological care essential for long-term management.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care for Rosacea Management
Managing rosacea requires more than medication alone. Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is a key part of controlling flare-ups. Patients are advised to use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products and broad-spectrum sunscreen daily. Stress management, avoiding extreme temperatures, limiting spicy foods and alcohol, and maintaining a consistent skincare routine can significantly improve symptoms. Keeping a symptom diary can help identify triggers and patterns, allowing patients to take proactive steps in preventing future flare-ups.
When to See a Dermatologist
If facial redness, bumps, or irritation persist or worsen over time, it is important to consult a dermatologist. Early intervention can prevent rosacea from progressing and causing permanent skin changes. A dermatologist can provide an accurate diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatments, and guide patients on skincare and lifestyle adjustments. Delaying professional care often leads to more severe symptoms that are harder to manage. Timely dermatological consultation can make a noticeable difference in both skin health and overall confidence.
Book Appointment with Best Dermatologist in Karachi via InstaCare
If you are experiencing ongoing facial redness, flushing, or acne-like breakouts, don’t ignore the signs of rosacea. Early diagnosis and expert treatment can help control symptoms and prevent complications. You can book an appointment with the best dermatologist in Karachi via InstaCare to receive personalized care, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment plans from experienced skin specialists.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a chronic but manageable skin condition that requires proper understanding, early diagnosis, and consistent care. While it may not be completely curable, the right combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and professional guidance can significantly reduce symptoms and improve skin appearance. If you suspect rosacea or notice persistent facial redness, seeking help from a qualified dermatologist is the best step toward healthier, calmer skin and long-term confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, rosacea and acne are different conditions. Although rosacea can cause acne-like bumps, it does not involve blackheads and has different underlying causes and treatments.
Rosacea does not usually go away without treatment. Symptoms may temporarily improve but often return and worsen without proper management.
Common triggers include spicy foods, hot beverages, alcohol, and foods that cause flushing. Triggers vary from person to person.