Ozone therapy has emerged as a fascinating alternative medical treatment, harnessing the power of ozone a triatomic form of oxygen (O3) to promote healing and combat various health conditions. Unlike the ozone layer high in the atmosphere that shields us from ultraviolet rays, medical ozone is generated specifically for therapeutic use, often through specialized machines that mix oxygen with electrical sparks to create controlled concentrations. This therapy dates back over a century, with roots in Europe during the late 19th century when scientists first explored ozone’s disinfectant properties.
At its core, ozone therapy introduces ozone gas into the body via multiple methods, triggering biological responses that enhance oxygen delivery, modulate the immune system, and fight pathogens. Proponents highlight its potential in treating chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, and even supporting recovery from long COVID. However, it’s essential to approach it with an informed perspective, as while anecdotal successes abound, rigorous clinical evidence varies. This article delves into why people turn to ozone therapy, its types (including variations like ozon therapie popular in German-speaking regions), advantages, specific benefits, procedural steps, and more, drawing from scientific studies and expert insights to offer a balanced view.
In an era where conventional medicine sometimes falls short for complex, persistent ailments, ozone therapy appeals to those seeking integrative options. It aligns with holistic health trends, emphasizing the body’s innate healing capacity. As we explore its benefits, we’ll uncover how this therapy might bridge gaps in treatment, backed by mechanisms like improved oxygenation and antioxidant effects.
People opt for ozone therapy when standard treatments yield limited results, particularly for conditions resistant to antibiotics or anti-inflammatories. Chronic fatigue, Lyme disease, viral infections, and degenerative issues like arthritis drive interest, as ozone’s oxidative properties target root causes rather than symptoms.
One key reason is its broad-spectrum antimicrobial action. Ozone disrupts bacterial cell walls, viral envelopes, and fungal structures without fostering resistance a major edge over pharmaceuticals. Studies, such as those in the Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine, show ozone inactivating pathogens at concentrations safe for human tissues.
Ozon therapie, as it’s termed in European practices, gained traction post-World War I for wound healing, evolving into a staple for immune modulation. Patients with autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis report reduced flare-ups, attributing it to ozone’s cytokine-balancing effects. For athletes, it accelerates recovery by boosting circulation and reducing lactic acid buildup.
Accessibility plays a role too clinics worldwide offer sessions costing $100–300, often more affordable than prolonged drug regimens. Those wary of side effects from steroids or chemotherapy find ozone’s minimal invasiveness appealing. A 2020 review in Medical Gas Research noted its adjunctive value in cancer care, enhancing chemotherapy efficacy while mitigating toxicity.
Skeptics point to regulatory hurdles; the FDA approves ozone only for disinfection, not systemic therapy, deeming it unproven. Yet, in countries like Germany, Russia, and Cuba, it’s integrated into protocols. Why choose it? For empowerment patients often feel proactive, combining it with diet and lifestyle changes for synergistic gains.
Emerging research on post-viral syndromes, like long COVID, underscores timeliness. A 2023 Italian study in Frontiers in Medicine reported symptom relief in 80% of patients after rectal insufflation. Ultimately, it’s about personalized medicine: when diagnostics reveal oxidative stress or hypoxia, ozone addresses these biochemically.
Ozone therapy isn’t one-size-fits-all; diverse administration methods tailor it to conditions, patient tolerance, and practitioner expertise. Here’s a breakdown of the main types.
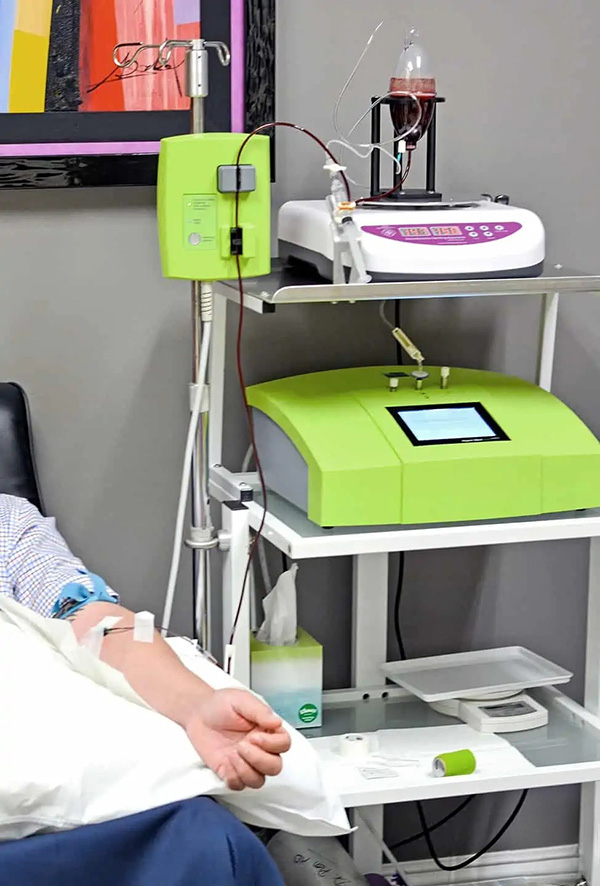
The gold standard involves drawing 50–200ml of blood, mixing it with ozone in a sterile bottle, and reinfusing it intravenously. This exposes blood cells directly to ozone, activating red blood cells for better oxygen release. Ideal for systemic issues like infections or autoimmunity.
Similar but smaller scale: 5–10ml blood ozonated and injected intramuscularly. It’s quicker, suited for immune stimulation in allergies or fatigue.
Ozone gas is introduced via a catheter into the rectum, absorbed through the gut mucosa. Non-invasive and popular for gut health, IBS, or Crohn’s, with studies showing microbiome improvements.
Vaginal or Bladder Insufflation
Targeted for gynecological or urinary infections. Ozone flushes pathogens locally, with high success in recurrent UTIs per a Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases report.
Ozon Apherese (Ozone Apheresis)
A sophisticated variant, apherese (or plasmapheresis) extracts blood, separates plasma, ozonates it, and returns it. Used in severe cases like sepsis or ozon therapie protocols for detoxification. European clinics favor it for chronic fatigue syndrome, citing enhanced clearance of toxins.
Subcutaneous or Intra-Articular Injections
Ozone injected into joints for osteoarthritis or soft tissues for pain. Prolozone therapy combines it with nutrients for ligament repair.
Ozone oil, water, or bagging for wounds, herpes, or skin conditions. Dentists use ozonated water for cavities.
Ear, Sinus, or Rectal Variations
For ear infections or sinusitis, gas flows gently into cavities.
Each type varies in ozone concentration (10–60 mcg/ml), with MAH and apherese offering deepest penetration. Selection depends on diagnosis e.g., insufflation for GI woes, injections for musculoskeletal pain.
Ozone therapy stands out for its multifaceted advantages over traditional interventions.
First, versatility: it tackles inflammation, infection, and circulation issues simultaneously. Unlike antibiotics that spare viruses/fungi, ozone’s free radicals attack all microbes indiscriminately.
Second, immune modulation. Low-dose ozone upregulates antioxidants like glutathione, downregulates pro-inflammatories. A Redox Biology study (2021) showed Nrf2 pathway activation, mimicking caloric restriction’s anti-aging effects.
Third, safety profile. When administered correctly, side effects are rare mild Herxheimer reactions (detox flu) at most. Contraindications like G6PD deficiency are screenable. Herxheimer is transient, unlike drug toxicities.
Fourth, cost-effectiveness. Sessions are brief (20–45 minutes), reducing overhead. Adjunctive use cuts antibiotic reliance, curbing resistance.
Fifth, non-pharmacological appeal. No liver/kidney burden, ideal for polypharmacy patients.
Ozon therapie protocols, including apherese, excel in outpatient settings, minimizing hospitalization. Enhanced oxygenation improves athletic performance; a German trial noted 20% VO2 max gains.
Environmentally, ozone generators are sustainable, using ambient air. Patient-reported outcomes shine: 70–90% satisfaction in surveys from the International Ozone Association.
The benefits span categories, substantiated by mechanisms and studies.
Antimicrobial and Antiviral Effects
Ozone’s ozonides perforate microbial membranes. Effective against HIV, hepatitis, and herpes; a Cuban study cured 100% of herpes zoster cases.
Anti-Inflammatory and Pain Relief
Reduces prostaglandins, easing arthritis pain. Knee osteoarthritis trials show 50% mobility gains.
Stimulates white cells, balances Th1/Th2. Beneficial for MS, lupus.
Improved Circulation and Oxygenation
Ozone converts hemoglobin to ferryl, enhancing tissue perfusion. Aids diabetes, peripheral artery disease.
Accelerates granulation; diabetic ulcers heal 2x faster.
Induces apoptosis in tumor cells, sensitizes to chemo. No standalone cure, but quality-of-life booster.
For Alzheimer’s, stroke recovery—neuroprotective via BDNF upregulation.
Binds lipopolysaccharides, aiding liver function.
Ozon apherese shines in sepsis, removing cytokines. Ozon therapie benefits chronic Lyme, with 75% symptom resolution in cohorts.
Steps Involved in Ozone Therapy
Undergoing ozone therapy follows a structured process for safety.
For apherese, dialysis-like machine processes 1–3 liters blood over 1 hour.
Ozone therapy offers compelling benefits from microbial annihilation to immune harmony positioning it as a valuable integrative tool. While not a panacea, its mechanisms, backed by decades of use in ozon therapie and advanced methods like apherese, warrant consideration for stubborn conditions. Consult certified practitioners; combine with lifestyle tweaks for optimal results. Future RCTs may solidify its place in mainstream medicine.
What conditions does ozone therapy treat best?
Chronic infections, pain, autoimmunity.
Is ozone therapy safe?
Yes, with proper dosing; rare risks like embolism avoided by experts.
How many sessions?
6–20, depending on issue.
Does insurance cover it?
Rarely; out-of-pocket.
Differences between ozon therapie and standard?
Ozon therapie emphasizes European protocols like apherese.